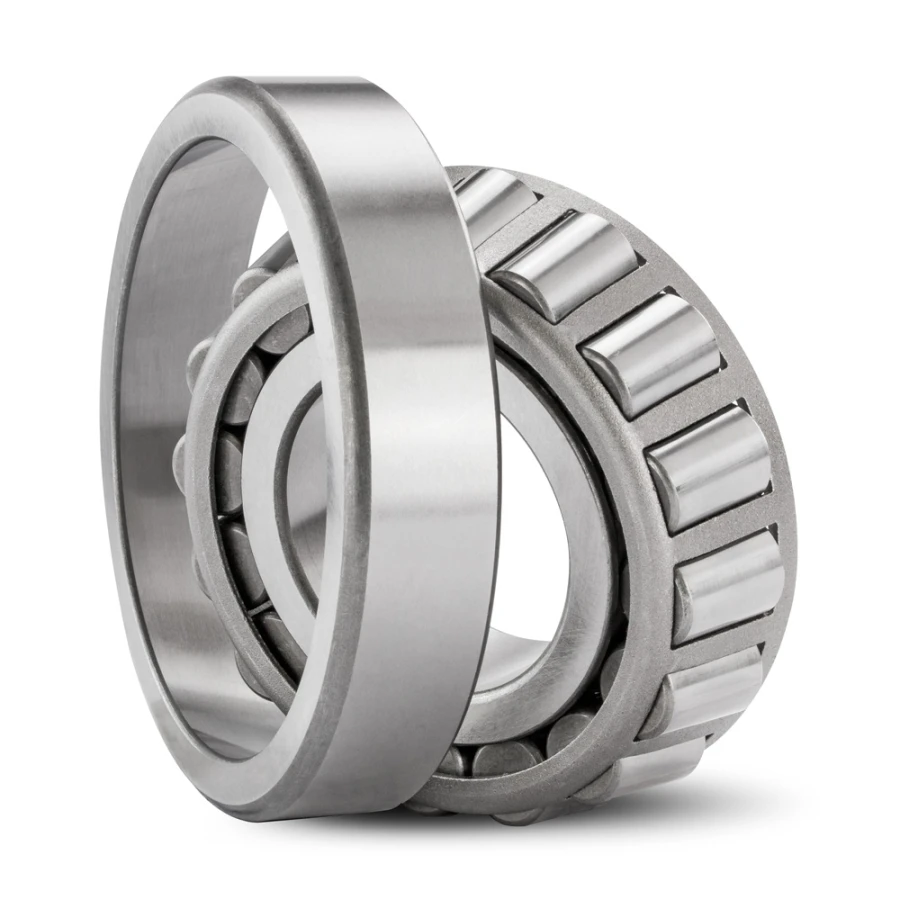
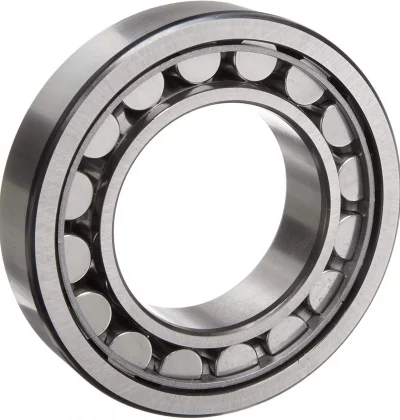
Product Description
Product Description
Product application
Certifications
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
Q:What’s your after-sales service and warranty?
A: We promise to bear the following responsibility when defective product is found:
1.12 months warranty from the first day of receiving goods;
2. Replacements would be sent with goods of your next order;
3. Refund for defective products if customers require.
Q:Do you accept ODM&OEM orders?
A: Yes, we provide ODM&OEM services to worldwide customers, we are CZPT to customize housings in different styles, and sizes in different brands, we also customize circuit board & packaging box as per your requirements.
Q:What’s the MOQ?
A: MOQ is 10pcs for standardized products; for customized products, MOQ should be negotiated in advance. There is no MOQ for sample orders.
Q:Do you offer free samples?
A: Yes we offer free samples to distributors and wholesalers
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Aligning: | Non-Aligning Bearing |
|---|---|
| Separated: | Unseparated |
| Rows Number: | Single |
| Load Direction: | Radial Bearing |
| Material: | Bearing Steel |
| Rotations: | Smoothy |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
What are the Steps for Proper Installation and Alignment of Tapered Roller Bearings?
Proper installation and alignment of tapered roller bearings are essential to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. Incorrect installation can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and even catastrophic failure. Here are the steps to follow for the correct installation and alignment of tapered roller bearings:
- 1. Clean and Prepare the Components:
Thoroughly clean the bearing components, including the bearing housing, shaft, and associated parts. Remove any dirt, debris, or old lubricant that could impact the bearing’s operation.
- 2. Choose the Correct Tools:
Use appropriate tools and equipment for the installation, such as bearing heaters for controlled heating and proper fit. Avoid using excessive force or striking the bearing directly, as this can damage the components.
- 3. Inspect the Bearings:
Before installation, visually inspect the tapered roller bearings for any signs of damage or defects. Ensure that the rollers and raceways are clean and free from contaminants.
- 4. Apply Lubrication:
Apply the recommended lubricant to the rollers, raceways, and other bearing components. Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing premature wear.
- 5. Mount the Bearings:
Mount the bearings onto the shaft or into the housing using appropriate methods. Avoid applying excessive force directly to the bearing components, as this can lead to damage. Utilize specialized tools like bearing pullers and press tools if necessary.
- 6. Ensure Proper Alignment:
Proper alignment is critical to prevent excessive loads, misalignment, and premature wear. Use precision measurement tools to ensure the bearing is aligned with the shaft and housing within specified tolerances.
- 7. Apply Controlled Heat:
If necessary, apply controlled heat to the bearing components to aid in expansion and facilitate proper fit. Ensure that the heat is applied uniformly to avoid distortion or damage.
- 8. Use Adequate Preload:
If specified for your application, apply the appropriate axial preload to eliminate internal clearance and optimize load distribution among the rollers.
- 9. Secure Bearings:
Secure the bearings in place using locking mechanisms, such as locknuts, to prevent unintended movement and ensure proper retention.
- 10. Verify Fit and Function:
After installation, verify that the bearings are properly seated, aligned, and functioning as intended. Rotate the shaft to ensure smooth operation and absence of unusual noise or vibration.
- 11. Document the Installation:
Keep a record of the installation process, including alignment measurements, preload values, and any relevant notes. This documentation can aid in future maintenance and troubleshooting.
Proper installation and alignment are essential to achieving optimal performance and longevity from tapered roller bearings. Following these steps ensures that the bearings operate smoothly and reliably within their intended applications.
What is the impact of proper lubrication on the performance and lifespan of cylindrical roller bearings?
Proper lubrication plays a crucial role in the performance and lifespan of cylindrical roller bearings. Lubrication is essential for reducing friction, minimizing wear, dissipating heat, and preventing corrosion. Let’s explore the impact of proper lubrication in more detail:
- Friction Reduction:
Proper lubrication forms a thin film of lubricant between the rolling elements and raceways of cylindrical roller bearings. This lubricant film separates the surfaces and reduces direct metal-to-metal contact. As a result, friction and sliding resistance are significantly reduced. The reduction in friction helps to minimize energy loss, improve efficiency, and reduce wear on the bearing components.
- Wear Prevention:
Lubrication creates a protective barrier between the rolling elements and raceways, preventing excessive wear. The lubricant film prevents metal-to-metal contact and acts as a cushion, absorbing shock and distributing the load evenly. By reducing wear, proper lubrication helps to prolong the lifespan of cylindrical roller bearings, ensuring reliable performance over an extended period.
- Heat Dissipation:
During operation, cylindrical roller bearings generate heat due to friction. Proper lubrication helps dissipate this heat by carrying it away from the bearing surfaces. The lubricant absorbs and transfers the heat, preventing excessive temperature buildup that could lead to premature failure. Effective heat dissipation through proper lubrication helps maintain the bearing’s operational stability and prevents thermal damage.
- Prevention of Corrosion:
Lubrication acts as a protective layer, preventing the direct contact of moisture or contaminants with the bearing surfaces. This barrier helps to inhibit corrosion and the formation of rust on the bearing components. By keeping the surfaces clean and protected, proper lubrication aids in maintaining the integrity and longevity of cylindrical roller bearings, especially in challenging environments.
- Noise Reduction:
Proper lubrication contributes to reducing noise and vibration in cylindrical roller bearings. The lubricant film acts as a cushion, damping the vibrations and reducing the generation of noise during operation. This is particularly important in applications where noise reduction is critical, such as precision machinery or equipment operating in quiet environments.
- Contamination Control:
Proper lubrication helps in controlling and minimizing the ingress of contaminants into cylindrical roller bearings. The lubricant forms a barrier that helps prevent the entry of dirt, dust, and other particles that could lead to premature wear or damage. By maintaining cleanliness, proper lubrication enhances the overall performance and reliability of the bearing.
In summary, proper lubrication is essential for optimizing the performance and extending the lifespan of cylindrical roller bearings. It reduces friction, minimizes wear, dissipates heat, prevents corrosion, reduces noise, and controls contamination. Bearing manufacturers and operators must follow recommended lubrication practices, including selecting the appropriate lubricant type and viscosity, ensuring proper lubricant replenishment, and adhering to scheduled maintenance intervals, to maximize the benefits of lubrication and ensure the long-term reliability of cylindrical roller bearings.
How do cylindrical roller bearings differ from other types of roller bearings?
Cylindrical roller bearings possess distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of roller bearings. Let’s examine the key differences between cylindrical roller bearings and other common roller bearing types:
- Design and Structure:
Cylindrical roller bearings feature cylindrical rollers that have a high length-to-diameter ratio. This design allows them to accommodate high radial loads and moderate thrust loads. In contrast, other types of roller bearings, such as spherical roller bearings or tapered roller bearings, have different roller shapes and configurations tailored for specific load and application requirements.
- Load Capacity:
Cylindrical roller bearings excel in handling radial loads. Their cylindrical roller arrangement and large contact area with the raceways enable them to distribute loads evenly along the rollers’ length. This characteristic makes cylindrical roller bearings suitable for applications where the primary load is radial. In comparison, other roller bearing types may be better suited for applications with different load orientations or combinations of radial and axial loads.
- Thrust Load Capability:
While cylindrical roller bearings can accommodate moderate axial loads, they are primarily designed for radial load-carrying capacity. On the other hand, thrust roller bearings, such as spherical roller thrust bearings or tapered roller thrust bearings, are specifically designed to handle predominantly axial loads. These thrust bearings have different roller arrangements and structures optimized for axial load resistance.
- Internal Clearance:
Cylindrical roller bearings offer a range of internal clearances, which is the space between the rolling elements and raceways when no external load is applied. The internal clearance affects factors such as running accuracy, thermal expansion, and the ability to accommodate misalignment or axial displacement. In contrast, other roller bearing types may have different clearance options or incorporate specific features, such as preloading, to optimize performance in their respective applications.
- Application Diversity:
Cylindrical roller bearings find extensive use in various machinery applications, including electric motors, gearboxes, pumps, and compressors. However, other roller bearing types have their own advantages and are commonly employed in specific industries or applications. For instance, needle roller bearings are suitable for applications with limited radial space, while crossed roller bearings are commonly used in precision machinery that requires high positioning accuracy.
- Operating Speed:
Cylindrical roller bearings can operate at high speeds, depending on their design and internal clearance. Manufacturers provide speed ratings and guidelines to ensure proper selection and operation within the bearing’s speed limits. Other roller bearing types may have different speed capabilities based on their specific design features, such as the shape of the rollers, cage design, or lubrication requirements.
Understanding the differences between cylindrical roller bearings and other types of roller bearings is crucial for selecting the appropriate bearing for a given application. Factors such as load requirements, load orientation, speed, space limitations, and environmental conditions should be carefully considered to ensure optimal bearing performance and longevity.
editor by CX 2024-04-30